Study of Wash-Induced Performance Variability in Embroidered Antenna Sensors for Physiological Monitoring
May 22, 2025
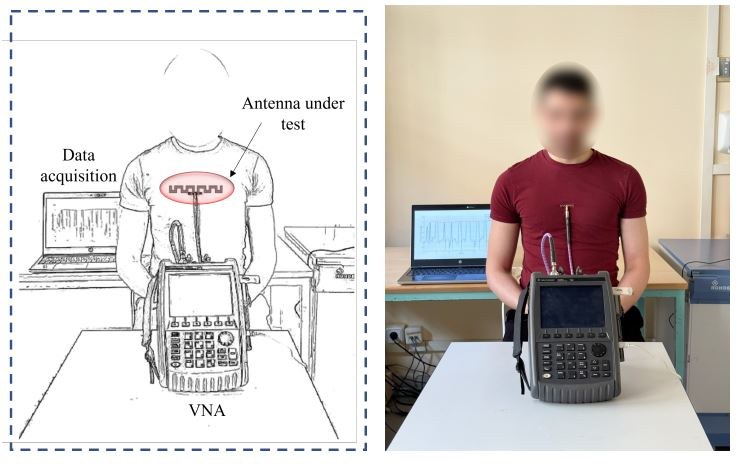
This paper presents a study on the repeatability of washing effects on two antenna-based sensors for breathing monitoring. One sensor is an embroidered meander antenna-based sensor integrated into a T-shirt, and the other is a loop antenna integrated into a belt. Both sensors were subjected to five washing cycles, and their performance was assessed after each wash. The embroidered meander antenna was specifically compared before and after washing to monitor a male volunteer’s different breathing patterns, that is, eupnea, apnea, hypopnea, and hyperpnea. Stretching tests were also conducted to evaluate the impact of mechanical deformation on sensor behavior. The results highlight the changes in sensor performance across multiple washes and stretching conditions, offering insights into the durability and reliability of these embroidered and loop antennas for practical applications in wearable health monitoring. The findings emphasize the importance of considering both washing and mechanical stress in the design of robust antenna-based sensors.
Share: